
When it comes to testing the purity of chemicals for various applications in the medical and pharmaceutical community, the right testing matters. You want to be compliant with all laws and regulations of the company, whether your company is mostly into the lab work of most projects or you're involved in the final completion of products and medical services, chemicals in the air can pose a safety risk and hazard. You can also be in health violation if chemical purity is not up to par.
Laboratories often replace their fume hoods for one main purpose: old age. The replacement process is something that is a concern of around 20% of laboratory owners and a third of the fume hoods replaced are old and outdated. You don't want to put your lab technicians or other professionals at risk of injury or inhaling potentially harmful fumes, so you should consider assessing chemical purity in your establishment. Here are reasons why this matters, even if you feel like you are already abiding by all guidelines.
Your Labs May Not Be As Safe As You Think
While you have never had any quality control issues before when you do your regular routine of assessing chemical purity, you still don't know if you are up to code with everything. GMP quality assurance is essential to operating a safe and legal laboratory so you should have the chemicals tested and have air quality assessed on the regular. This can be done in accordance with the recommendations of your quality specialist, or you can do this measure as recommended by your local state laws.
Your Labs Get Fully Tested for Quality
The best way to ensure the safety of your establishment is to have records that you work hard to keep your laboratory updated and sound. When you work with a variety of different chemical manufacturers and want to make sure you aren't imposing on chemical purity in any way, you can help make your establishment more attractive for research and testing purposes. Universities, independent pharmacies, and other establishments may see your company in a better light and extend their service needs to your lab over others in your community.
However you want to improve the safety of your laboratory, you can do so by having your chemical purity tests done on the regular. Your specialist will be able to give you what you need for accurately assessing chemical purity in your office, labs, pharmaceutical sectors, and more.
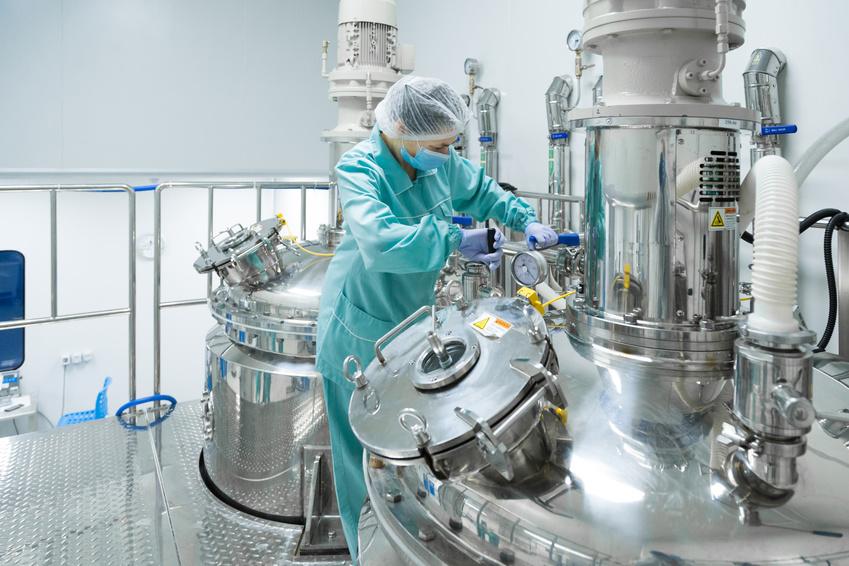

Over the years, the pharmaceutical industry has grown in leaps and bounds. Today, they have been able to formulate high-quality drugs to eradicate some of the deadliest diseases in the world and control the rest. The acceptability and efficacy of these drugs is reliant on the purity of the chemical substances used for medicinal effect also known as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs).

The United States stands as the largest chemical producer in the world. However, the accolades should be directed to the chemical manufacturers who are involved in mixing these chemicals and coming out with a particular chemical that is used for a particular role. These manufacturers are always involved in a hard and complex task of determining chemical purity. It's important to highlight that an impure chemical could have devastating impacts on the users, especially in the medical sector, where people use chemicals for medical purposes. But how do chemical manufacturers assess purity?
Assessing chemical purity is a complex task that involves incorporation of several styles and techniques that will give clear information on the composition of a particular chemical. The most important activity in determining chemical purity is understanding the specific components of a particular chemical and its physical or chemical properties. Some of the strategies used by chemical manufacturers to determine the purity of chemicals have been discussed below.
1. Use of Radiolabeled compounds
Radiolabeled compounds are carbon compounds that are used in chemical and biochemical processes of understanding the chemical constituents of a particular compound. Radiolabeled compounds are mostly used in the drug development stage and help in highlighting the compound formed after two or more molecules combine. Therefore, in a chemical process, radiolabeled compounds will be very useful in highlighting the physical and chemical properties of a particular product that has resulted after two or more chemicals combine. It is important to highlight that drug manufacturers know drugs by assessing physical and chemical properties.
2. Physical Comparison with Pure Standard
Physical comparison has been used in understanding the purity of a particular compound. It is the simplest method of checking purity as it only involves comparing a particular chemical with a certified pure sample. There is an argument against the use of physical comparison, but it is obvious that this method can show significant differences between products. Physical comparison is very useful in revealing large impurities such as colored impurities and dirt. Smell tests will also reveal the differences between the chemical undergoing tests and the actual and pure state of a particular compound. However, it's important to note that only non-toxic chemicals can be tested through touch, taste, and smell.
3. Boiling and Melting Point Determination
It is obvious that the physical properties of a chemical can be used to indicate whether it is pure or not. Most of the chemical products have defined boiling and melting points. Pure chemicals are known to boil and melt at specific temperatures, and that is documented. However, if the melting point of a particular chemical is lowered, there is a great sense that the chemical is not pure. The boiling point will be higher than normal. This is a simple method of determining the purity of a product and is highly applied in various chemical manufacturing plants.
4. Colorimetric Methods
The colorimetric method is another widely used strategy of determining the purity of a chemical compound. Biochemically, some chemical compounds change into a particular color when they are exposed to a certain chemical. This is widely known, documented, and used as a standard way of determining the purity of various products. One of the major applications of the colorimetric method is in determining the presence of specific illegal drugs such as cocaine and heroin. Colorimetric purity testing is highly preferred because it does not only indicate the purity of a chemical but also the percentage purity.
5. Analytical Testing
Although other methods of testing purity are highly appropriate and advanced, analytical testing is the most accurate and highly preferred method of testing chemical purity. Analytical testing involves a standard procedure that is used in testing various chemicals. These procedures are applied in drug and chemical industries, and they indicate the presence and the number of impurities. Some of the analytical purity testing methods include titration, infrared spectroscopy, paper chromatography, and optical rotation, among others.
These are some of the strategies used in testing the presence of impurities in chemical compounds. However, the method that one applies depends on the resources available, the magnitude of the entire process, and the chemical under consideration. However, any method is likely to indicate the presence of impurities in a particular chemical.
Isotopic Labeling
Radiocarbon dating, the backbone of Isotopic Labeling, was developed by physicist Willard F. Libby in the 1940s. Over the last 80 years, there have been a number of advances that have increased the scope and application of Libby's method. This is mostly done with radiolabeling.

The U.S. holds over 45% of the global pharmaceutical market. Our dominance of scientific and medical fields has allowed us to raise the bar when it comes to the development and circulation of life-saving and life-changing medications. Before these medicines can be offered to the general public, however, they must undergo a grueling testing period; clean room standards must be met to ensure that they aren't tainted or contaminated. From GMP storage conditions to GMP quality control, there are a number of steps and tools that play a major role in this sterile environment. Let's take a look at some of the benefits that ductless fume hoods in particular offer.

The U.S. is the number one largest national producer of chemical products in the world. Our scientific and medical advancements -- and dedication to GMP standards and GMP quality control -- allow us to dominate the market; everything from radiolabeled compounds (Tritium, a radioactive isotope of hydrogen, is often used) to GMP synthesis originates in this country. With the new tariffs on Chinese imports, however, that may change.

Storage Conditions and Chemical Purity
Why are storage conditions for drugs so important? How do chemical manufacturers assess purity of chemicals they use for drugs? Why should you care?
(more…)
The U.S. is the number one largest national producer of chemical products in the entire world. Although we continue to push the limits on what can and cannot be done (radiolabeled compounds allow us to treat illnesses with a high degree of accuracy), it isn't an accident that we won that incredible top spot; our dedication to good manufacturing practices -- through GMP storage, GMP synthesis, and overall clean room standards -- has ensured that we stay protected from contaminants that could compromise our products.

The U.S. pharmaceutical sector is utterly massive. Thanks to its 810,000 employees, our nation is able to hold over 45% of the global pharmaceutical market. However, we didn't get to the top on sheer dumb luck; our strict adherence to clean room standards and good manufacturing practices (GMP) has ensured that all of our work -- from radiolabeling and carbon 14 production to GMP synthesis (guanosine monophosphate) -- follows GMP standards and GMP storage conditions.
Every day, scientific advancements are being made. From new treatments to innovative diagnostic tools, the world of medicine is constantly changing; radiolabeling is at the forefront of these remarkable developments, especially where cancer is concerned.
The U.S. is at the forefront of innovation when it comes to medicine. In fact, this great nation holds over 45% of the global pharmaceutical market. Because of this commitment to science and the advancement of health, new drugs and chemicals are constantly becoming available to the public.
However, these chemical concoctions must be run through the gamut to ensure they are safe to use and consume. There are a variety of GMP quality control steps and GMP synthesis standards in place to reduce the possibility of contamination (such as the many clean room standards), but the risks associated with chemical impurities are just as dangerous; let's take a look at five of them.
- Impurities: Impurities are defined as any component that is not the chemical entity of the new drug substance. These could be organic or inorganic in nature, and can even result from the degradation of the product. The risk here is that some impurities may be extremely toxic.
- Overdose: If a mistake occurs in the new drug substance that results in too many of a single chemical, the body may overdose. Even the most beneficial drugs can become harmful if too many are consumed; although overdose is rare, it is a danger of chemical impurities.
- Sterility: In parenteral products -- where the drug is injected directly into the bloodstream -- the bodies natural defenses are completely bypassed. Sterility has to do with contamination; because you're skipping these crucial opportunities for defense, a parenteral product that is not sterile could seriously harm the patient.
- Endotoxins: Endotoxins refer to toxins that are present inside a bacterial cell that get released when the cell breaks down. Historically speaking, exposure to endotoxins causes a wide spectrum of nonspecific pathophysiological reactions, such as fever, changes in white blood cell counts, hypotension, shock, and death.
- Particulates: In a new drug substances that is parenteral, the presence of particulates can be incredibly dangerous. Since having fibers, dust, rubber, and silicone pumping through your veins can cause a variety of negative side effects, ensuring that particulates are eliminated is essential.
Many people wonder, "how do chemical manufacturers assess purity?" At the end of the day, it's not how they do it, it's that they're doing it at all; because of the precautions established by GMP quality assurance procedures, knowing "how do chemical manufacturers assess purity" is irrelevant to your safety.

Clean rooms are used in a variety of fields, though they are absolutely vital when it comes to medicine. By eliminating every possibility of contamination -- whether it be biological, chemical, or physical in nature --, scientists and researchers can guarantee that their work (and the people who depend upon it) is untainted. From drug development to manufacturing, every step of the process must abide by strict clean room standards.
Though there are many different clean room standards (including the care and use of fume hoods) that should be met, this article is going to focus on the four main characteristics that clean room clothing should follow. Let's take a look.
- Non-linting material: Regular clothing is full of small fibers that occasionally fall loose. While this is not a problem in normal life, these minuscule fibers can damage delicate machinery; clothing that is lint-free does not experience the same problem.
- Resistance to arc flashes: If the threat of an electrical arc flash is present, OSHA requires employees to wear clothing that won't immediately catch on fire in the event they come into contact with it. Since arc flashes can exceed 35,000 degrees Fahrenheit, it's vital that flame-resistant clothing be worn for protection.
- Anti-static carbon fibers: In oxygen-rich environments, even something as small as the shock from static electricity can pose a threat. Additionally, very sensitive electronic equipment can be damaged by static shocks, even those that cannot be detected by human beings. Anti-static or electrostatic discharge (ESD) clothing reduces this risk.
- High-density fabric: In a very simple way, thick, high-density fabric prevents corrosive liquids and heat from harming any lab technicians or scientists.
The risks are simply too high to chance skipping a single step in the interest of saving time. In 2012, 48 people died when a pharmacy in the northeast failed to commit to clean room standards and accidentally infected a common prescription drug with fungal meningitis; in 2008, a staff researcher died after being burned because she was not wearing lab attire and was handling a chemical that ignites spontaneously in air.
Whether you're dealing with radiolabeled compounds, ICN radiochemicals, or sensitive drugs, you should always be wearing gear that follows the above design characteristics. Otherwise, you -- or dozens of people you've never met -- may suffer the consequences.
