
With today’s electronic sensing devices, the humidity of pharmaceutical cleanrooms can now be maintained and monitored with tolerances as small as one percent. Technology that helps monitor and control environmental factors is crucial for pharmaceutical, food, and cosmetic development, and related to these control factors is GMP quality control.
What Are GMP Standards?
Good manufacturing practices — GMP — are regulations set forth by the Food and Drug Administration to ensure that industries produce goods that are safe for civilian use. These regulations cover development, manufacturing, and storage, stipulating how processes should be completed, controlled, and monitored. Following GMP quality assurance protocols help industries maintain high standards and deliver products that have been tested thoroughly to ensure quality.
GMP quality control is crucial for establishing strong operating procedures that maintain the integrity of products. This is because of the stipulations regarding environmental conditions that correspond with testing and storage facilities. By ensuring that the highest standards are met during the testing, development, and storage stages, manufacturers can expect to mitigate testing failures, unnecessary contamination, errors related to environmental factors, and harmful deviations.
Why is GMP Quality Control Important?
GMP quality control measures are put in place and mandated by the government to ensure that pharmaceuticals, medical devices, food, and cosmetics, are safe for mass distribution. This helps ensure that none of the produced products contain harmful substances or contaminations that could otherwise cause problems to consumers. GMP quality control can also help mitigate the need for recalls or lawsuits that can arise should a faulty or defective product make it out into the market. For instance, GMP regulations were first enacted by the government in 1963, after thalidomide was nearly sold in the United States. Thalidomide had previously been linked to over 10,000 cases of birth defects in Europe and, without the resulting regulations, could have gone on to cause similar problems in the U.S.
Today the government enacted GMPs are more flexible and allow for manufacturer discretion within reason. This allows industries to collaborate and enact their own effective means for quality control and GMP storage conditions. Furthermore, this also allows manufacturers to take advantage of more technological advancements, as mentioned above, to ensure a greater level of control can be obtained throughout the development, manufacturing, and storage stages.
The Purpose of GMP Quality Controls
A consumer cannot, on their own, determine whether a drug, cosmetic, or food is effective or safe for application or consumption. One way manufacturers can help prevent defective products from making their way out into the market is by conducting testing at various stages of production. While this step can help, it also isn’t enough on its own. GMP protocols and training are essential for ensuring products are handled properly throughout the manufacturing process without risking contamination. All facilities should be well maintained and in good condition with hygiene and cleanroom guidelines strictly adhered to by all staff. Everyone should be trained in GMPs and know not to cut corners during any step of the process. Likewise, all equipment should be maintained, calibrated, cleaned, and verified as recommended and as needed. These facets are covered most by GMP regulations and adapting procedures to follow can improve product quality and ensure that risks of contamination and recall are mitigated.
How Do GMPs Differ from Other Quality Assurance Types?
While other methods of quality assurance exist, GMP is the only that is mandatory for manufacturers to follow. For instance, ISO quality certifications are encouraged but not required for manufacturers of food, drugs, or cosmetics. GMP is also the only one to include guidelines related to the verification of each process, preventative actions, the qualifications of vendors, and good laboratory practices, making it both thorough and comprehensive.
GMP quality control is essential for many industries, especially those that make topical or consumable products. Always be sure to know the guideless that affect your industry to avoid the risk of recall, lawsuits, or sanctions. Furthermore, if you utilize an outside storage facility, ensure that they too know GMP guidelines and how to follow them.

The United States produces more chemical products than any other country in the world. Pharmaceutical manufacturing involves the synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (API) according to good manufacturing practice (GMP). Companies that offer API GMP solutions, tritium (3H) labeling, and carbon 14 (c14) radiolabeling (labeling with a radioactive atom or substance) can manufacture carbon isotope 14 (14C) and tritium radiolabeled APIs. This allows studies to be conducted for the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) phases 0, I and II microdosing and mass balance. These companies perform API GMP tests for synthesis, purification, and other testing to comply with FDA guidelines. Companies that provide this testing may also offer GMP storage for customers' pharmaceutical compounds.
(more…)
Pharmaceutical companies are consistently involved in research and other activities to enhance their work. They want to come up with new drugs and other biotechnology solutions to provide better products to their customers. Because of that, they are constantly looking for GMP storage solutions such as those provided by Moravek. However, every person working in this industry has to know the factors that should be considered when choosing such services.
(more…)When choosing radiolabeled compounds you have many options; tritium, deuterium, carbon 13, nitrogen 15 and carbon 14. For many reasons, carbon 14 is one of the most popular choices in radiolabeling. With an impressive half-life of >5000 years, as compared to tritium’s half life of 12.5 years, carbon 14 has a low energy and is easy to detect with beta emissions.
(more…)
Maintaining GMP standards in laboratories is important not just for ensuring staff safety, but for ensuring contamination doesn’t spread to consumer products. A fungal meningitis outbreak was traced to a pharmacy where protocols and sanitation were being overlooked. By the time the drug was recalled 48 people had already died from the contaminated drug. GMP standards exist to prevent incidents like this from happening, and even in labs that focus primarily on custom radiolabeling, the same procedures apply. If you’re looking for radiolabeling services, ensuring you find a company that adheres to high GMP standards is key.
(more…)
In the United States, over 810,000 people are currently working in the chemical industry, including pharmaceuticals. If you are one of these individuals, then you understand how critical radiolabeled compounds can be to the testing process. Being able to track the metabolizing rate of drugs within the body is crucial for developing safe and effective drugs that could result in life saving discoveries. While many labs send samples off for radiolabeling, it’s important to know what to look for when it comes to selecting the right radiolabeling service for your needs.
(more…)
Radiolabeling is a scientific technique used to track the passage of a molecule. The technique incorporates a radioisotope through a reaction, cell, organism, biological system, or metabolic pathway. The reactant is labeled by replacing specific atoms by their isotope.
(more…)
Currently, the United States is responsible for 45% of the pharmaceutical market worldwide. With respect to this, GMP storage conditions are especially important in this industry. At a glance, GMP is a system that works to ensure that products are consistent and controlled with respect to quality standards. In the pharmaceutical industry, this helps minimize the risk of contamination and potentially dangerous mixups with products.
(more…)
The United States remains to be the leading producer of various chemicals associated with drugs, food additives, and preservatives. With this title come several challenges, such as accidents happening in various laboratories and chemical manufacturing plants. As a leader of a chemical producing plant, you already know the accidents associated with such chemicals, especially radiolabeled compounds.
(more…)
When you are creating pure, high quality radiolabeled compounds, you need to hold your production process to the absolute highest material and clean room standards possible. There is a reason Moravek was given two large grants by the National Institutes of Health -- it is due to strict adherence to Good Manufacturing Practice, or GMP.
(more…)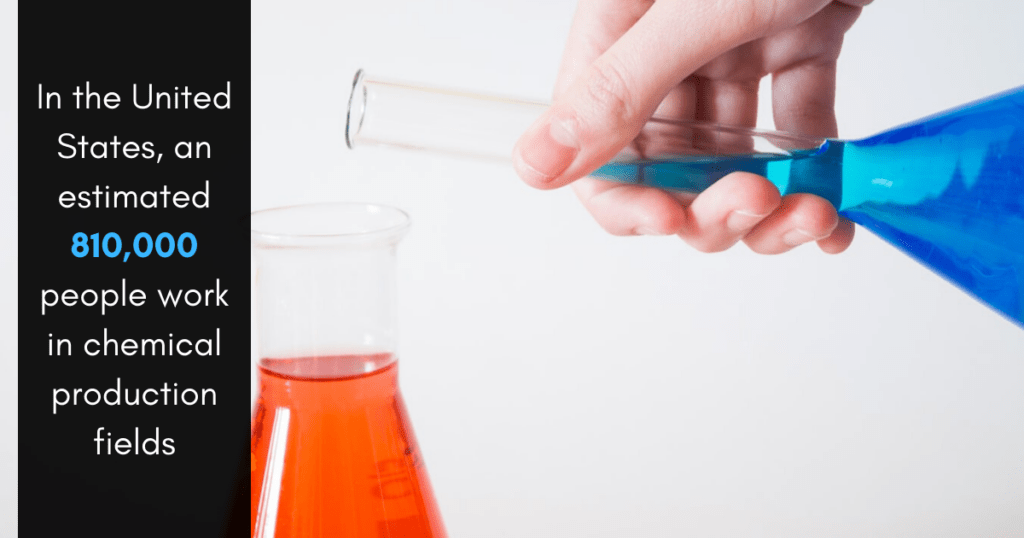
In the United States, an estimated 810,000 people work in chemical production fields, including the pharmaceutical sector. In this industry, C14 radiolabeling remains the standard and is the first choice for the labeling of active pharmaceutical ingredients. This type of labeling is crucial for API GMPs, as it permits more information to be collected pertaining to metabolism, distribution, adsorption, and excretion -- all of which can be critical to understanding the pharmaceutical during the clinical study stages.
It's important to note that, in recent years, APIs (along with their delivery methods) have increased in complexity as research has progressed and unearthed new discoveries. This means that radiolabeling now contains new challenges, which has prompted new technologies to be employed to ensure process efficiency.
(more…)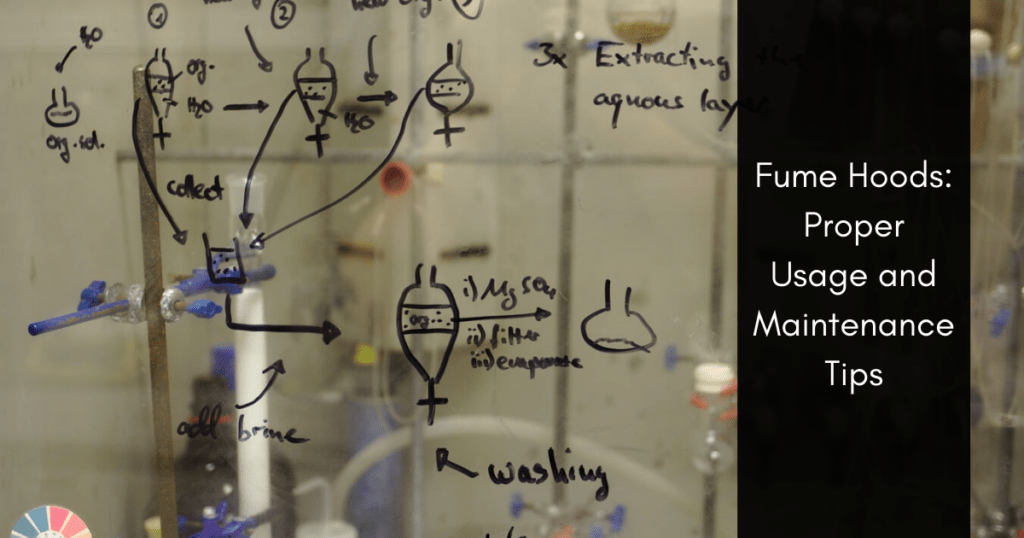
Fume hoods are an important part of any laboratory. Aiding in ventilation, these exhaust systems help remove harmful chemical fumes from the air (for instance, during radiolabeling or GMP synthesis) to better ensure the safety of scientists and personnel. Fume hoods are a crucial part of maintaining clean room standards and can prevent an excess amount of vapor, aerosol, gases, and dust from accumulating in the air.
(more…)