
In relative terminology, the word organic refers to anything that derives from or relates to living matter. Conversely, its antonym inorganic relates to anything not deriving from or consisting of living matter. This definition holds true within the scientific field of biology, but modern chemistry is a diverse subject. The essential basis of chemistry revolves around a dynamic duo—namely, that of organic and inorganic compounds. Scientifically, two distinct disciplines exist because of these divergent facets of matter-examining chemistry—that of organic chemistry and inorganic chemistry.
(more…)
An active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is an active component of a specified medicine. Throughout the process of pharmaceutical manufacturing, an API plays a critical role as a medicinal application agent. Each pharmaceutical product contains two core ingredients: inactive excipients that deliver the medicine to a target system and the APIs themselves.
(more…)
Pure substances are made up of a singular type of atom or a singular grouping of molecules. Within the context of chemistry, the means by which a substance is measured for this standard is known as purity. Pure substances have well-defined physical properties that establish their classification of purity. The importance of purity in chemistry lies in effective research and the safety of consumer usage. Purity standards relate directly to quality control in pharmaceutical production.
(more…)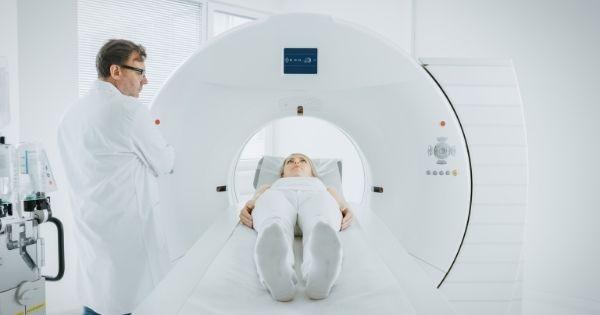
Since the onset of Homo sapiens’ time on planet Earth, humanity has sought out immeasurable methods to identify, utilize, and manipulate materials in the environmental world. The historical depictions of our most ancient civilizations and their actions analogously relates to the story of today’s most critical sciences. Early humankind used basic forms of chemistry to both create and preserve. Chemistry is the scientific study of matter and its various properties. Even with our ancestors’ limited knowledge of atoms and elements, chemistry occurred recurrently in the environment.
(more…)
Nuclear medicine techniques offer a wide array of diagnostic, research, and therapeutic applications. Radioactive isotopic labeling is a specific technique that assists during challenging regulatory and development projects. Within radiochemistry, synthetic radiochemists have the expert ability to produce stable radioactive isotope labels that support human clinical trials or pre-clinical research studies.
(more…)
Medical professionals and researchers extensively utilize radiolabeled pharmaceutical products for clinical studies. The comprehensive process of producing these radiolabeled compounds is a relatively delicate scientific technique—synthesis is a chemical technique calling for knowledge, caution, and care.
(more…)
The high demand for cleanrooms across worldwide industries culminates a pressing need for avant-garde growth, reconfiguration, and pioneering innovations. Most unambiguously, the pharmaceutical manufacturing industry has a compelling demand for the enhancement of cleanroom technology. At their core, cleanrooms are ideal means for good manufacturing practices that prevent contamination during high-standard research and production procedures.
(more…)
Nuclear medicine today is an advanced science providing a wide array of medical innovations and solutions. In particular, experts use radiolabeled compounds and various imaging technologies for drug research and development. However, these instrumental radioisotopes are scientific tools that help diagnose and treat complicated or life-threatening illnesses within controlled medical applications.
(more…)
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy is an imperative analytical tool for the research and development of pharmaceuticals. NMR spectroscopy is applicable in various stages of the drug development process to provide critical identification information. NMR also classifies drug impurities. Let’s examine closer the most widely-utilized applications of NMR in pharmaceutical analysis.
(more…)
Henry Becquerel, a French physicist, is said to be the first human to discover evidence of natural radioactivity—which is the spontaneous emission of radiation from a singular material. This natural force benefits humankind in an assortment of ways. The field known as radiochemistry exists today because of his initial discovery, and the advancements of the phenomenon ever since.
(more…)
Pharmaceutical quality affects every individual who takes medications, dietary supplements, or utilizes other drug products. Consumers assuredly expect that the drug they receive meets quality standards for safety and efficiency. To do so, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has established certain best practices called current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP). The manufacturing, packaging, and labeling of pharmaceuticals must follow these standards.
(more…)
Drug formulation is a complicated process. Apart from APIs—active pharmaceutical ingredients—inactive excipients play a key role in a drug’s development. In comparison to the primary components of APIs, pharmaceutical excipients are secondary components.
(more…)